The Wi-Fi Internet Speed is Lower. Who sores the router Cut the Speed?

Internet speed via wi-fi is a topic that has always been discussed and will be discussed on various forums, in comments, etc. Very often people ask questions like: “why the speed over Wi-Fi is lower than over cable”, “why the speed through the router is less”, “how to increase the speed of the Internet over wi-fi”, etc. Why this happens at all, where do these questions come from. Now I will explain.
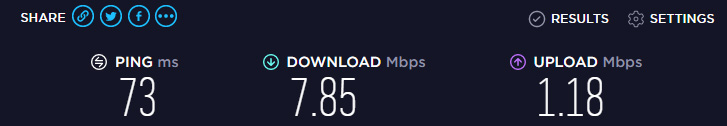
There is the Internet, which is connected to the computer directly. The provider promises a speed of for example 100 Mbps. When checking, the speed may be a little lower, but something about that. We buy a router, install it, and of course check the speed, because we read somewhere that the router cuts the speed. Check from the router on the cable, it seems normal, not much speed dropped. We check when connecting via wi-fi and see that the speed is two or more times lower than when connecting via cable. For example, on wi-fi from 100 Mbit/s that the provider gives, there are 50 Mbit/s, 40, or even less. Obviously, this does not suit us, and we start looking for a solution. And in search of a solution we go to pages like this one.
If you want to see specific tips on the topic of increasing speed on wi-fi, then I will write about it a little later, in a separate article. But, I want to say right away that the tips that I will write about, and that can already be found on the Internet, as a rule, do not give any results in terms of increasing speed. Although, it depends on individual cases. And in this article I just want to tell you why it happens that when you connect through a router, the speed of the Internet is slower than for example by cable.
Why Wi-Fi router cuts the speed?
Every router cuts the speed. Some less, some more. As a rule, it depends on the price of the router itself. The more expensive it is, the more powerful it is, and the more powerful it is, the less it will cut the speed. I am now talking about wi-fi connection. If the speed on the cable through the router and less, then as a rule, it is not critical. But on the wireless network, speed losses can be decent.
Many people are still interested in the numbers that are indicated on the box with the router, or in the characteristics. There you can see information on speed. For example: up to 150 Mbit/s, or 300 Mbit/s. And here again there are questions: “why does my router supports 300 Mbit/s, and I have a speed of 50 Mbit/s?”. Well, the manufacturer specifies the maximum speed, which you can never get under normal conditions. The speed will always be much lower. And with those 300 Mbps, which are written on the router, we often get a speed several times lower. And how much slower the speed will be depends on the router’s power (mostly), and on a number of other factors, which I will tell you about now.
Also, we should not forget that in addition to the router, we have a network wi-fi receiver in our laptop, tablet, smartphone, or USB/PCI adapter in a desktop computer. Which also supports different standards, and the speed at which it works may be lower than the one that can give the router. The speed is always determined by the slowest device on the network. For example: a router gives out a theoretical 300 Mbps. But the adapter that receives the signal can work at a maximum speed of 150 Mbps. And we already get a limitation of 150 Mbit/s, as in the network, this device is the slowest. Well, I will further delve into these nuances, I just wanted to explain why the speed suffers when connected to the wi-fi network.
What depends on the speed of wi-fi network, and how to get the maximum speed?
As promised, I will write in more detail about ways to increase speed in a separate instruction. And now, I will list the main reasons that affect the speed of Wi-Fi network:
- wi-fi router. Network standards (802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11as) that it supports, what technologies it uses, and the power of the hardware itself. As a rule of thumb, the more expensive the router, the faster the wireless speed.
- The software of the router, and the Wi-Fi receiver on your computer. Very often, with an update of the router firmware, or adapter drivers on your computer, the speed becomes faster.
- Interference. Interference can be from other, neighboring Wi-Fi networks (mostly), as well as from household appliances.
- Wi-Fi network power. It is not news that near the router, where the signal is maximum, the speed will be higher than in another room, where the network signal is no longer so stable.
- The number of devices connected to your network. If one device is connected to your router, it will receive all the speed that the router can give. If we connect one more device and start downloading something on it, the speed will be divided by 2, etc. In addition, all connected devices create a load on the hardware of the router, which leads to a drop in speed.
- The type of Internet connection your ISP uses. The fact is that if your ISP uses Dynamic IP or Static IP connection type, the router will cut the speed less than with PPPoE, L2TP and PPTP connections.
- Router settings. The correct setting of network protection, selection of network mode and channel width, as well as changing the channel, can slightly increase the speed.
How to organize a Wi-Fi network, so that the loss of speed would be minimal?
As for the Internet provider: if you have not yet connected the Internet, and if possible, then choose a provider that uses the connection technology Dynamic IP, or Static IP. This way it will be easier for the router, and it will be much easier to set up such a connection.
Choosing a router: if you want to minimize the loss of speed, you will have to spend on a router. I advise you to buy a router that can work at 5GHz (GHz), and support the new 802.11ac standard. The 5GHz frequency is practically free now, which means that there won’t be much interference. After all, for the most part, all Wi-Fi networks operate on 2.4GHz. And the new standard 802.11ac, even compared to the most popular at the moment 802.11n allows you to transmit information at speeds as high as 6.77 Gbps. This is of course in theory, with special equipment.
Devices that you will connect to the network: as I wrote above, the speed also depends on the clients of the network. It is desirable that your devices are new, with support for the modern standard 802.11ac, or at least 802.11n. If it is a computer, then update the driver of your Wi-Fi adapter. I wrote about this in a separate article.
Check your internet speed, share your results in the comments, and tell me if your router is cutting your speed. All the best!


 What is a router? How IS Wi-Fi Router Different from the Router?
What is a router? How IS Wi-Fi Router Different from the Router?  Do I Need to Pay for the Internet if I have a wi-fi router?
Do I Need to Pay for the Internet if I have a wi-fi router?  Seamless Wi-Fi. Fast Roaming (802.11r) in the Wi-Fi Mesh Systems Settings
Seamless Wi-Fi. Fast Roaming (802.11r) in the Wi-Fi Mesh Systems Settings  Two Repiters in One Wi-Fi Network. How to Connect Several Amplifiers to One Router?
Two Repiters in One Wi-Fi Network. How to Connect Several Amplifiers to One Router?