Network Adapters in the Windows Devices Manager

Windows Device Manager has a separate section called “Network Adapters” that displays all network adapters that are installed on the system. Most often these are network card (LAN), Wi-Fi adapter (WLAN), Bluetooth devices, and system adapters: TAP-Windows Adapter, Microsoft Virtual wi-fi, Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct, WAN Miniport, etc.
In this article, I want to talk about these adapters. What they are responsible for and how they work. What network adapters should be in the Windows Device Manager. How to add and remove them. Why network adapters are not displayed in Device Manager, are not removed, do not work, do not see Wi-Fi and Internet. In the same Device Manager these adapters are not seldom displayed with errors. For example, “code 31”. It happens that an exclamation mark, an arrow, or the icon itself is transparent near the adapter. This means that there are errors in the operation of this device, it is not working properly, or it is disabled.
I have the “Network Adapters” section in Device Manager looking like this (in Windows 10):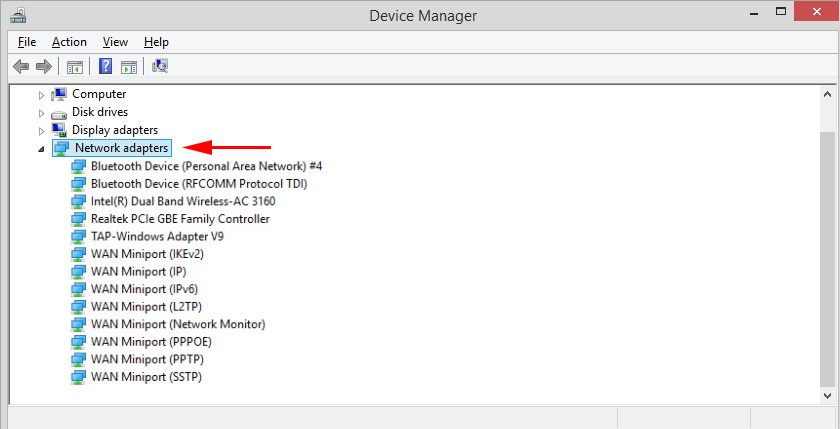
This is on a laptop with a Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module connected in addition to the network card. On a normal personal computer, for example, or on a laptop that does not have drivers for wi-fi and Bluetooth installed, this section may show only one adapter – the network card (I have Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller). Since Windows almost always automatically installs a driver for the network card. And it is in almost every system unit and laptop. Although, there are now many laptops without a network card.
Article on the topic: why there is no network adapter in Device Manager.
Let’s take a closer look at each adapter and understand what it is for and how it works. I will consider the example of adapters in my laptop.
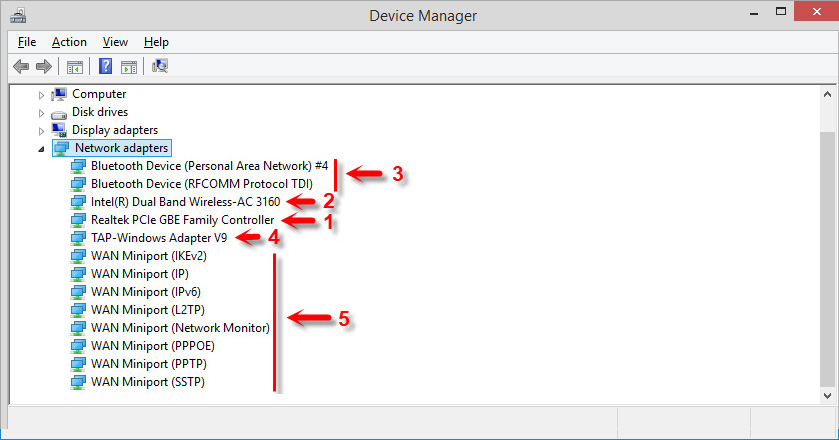
- Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller is a network card ( LAN) from the manufacturer Realtek (in my case). It is needed to connect to the internet using a network cable that plugs into the Ethernet port on your laptop, or PC. It usually has the words “PCI-E”, or “Ethernet” in its name. The most popular manufacturers of these controllers are Realtek, Qualcomm Atheros, and Intel. If this adapter is not in the Device Manager, then it is either not installed (or broken) or the driver is not installed.
- Intel(R) Dual Band Wireless-AC 3160 is a Wi-Fi adapter. Through it we connect to Wi-Fi networks. On laptops it is usually built-in. But on PCs you have to buy and connect a USB or PCI adapter. If you have a desktop computer, see the article how to choose a Wi-Fi adapter for PC. Words that can be used to identify a Wi-Fi adapter: “WLAN”, “Wireless”, “AC”, “Dual Band”, “802.11”. Manufacturers may be different: Intel, Atheros, Broadcom. If you don’t have such an adapter in Device Manager, it is not connected/broken/no driver installed. Very often the problem is with the drivers. Therefore, you may find this article useful: how to install drivers for Wi-Fi adapter in Windows 7.
- Bluetooth Device (personal area network) – these adapters are not responsible for Bluetooth operation, but for organizing a local network via Bluetooth, through different protocols. There can be several of them. If there are no such adapters, then you do not have a Bluetooth adapter connected, it is not configured, or you have not set up such a network.
- TAP-Windows Adapter V9 is a virtual Windows network adapter. It can be used for different tasks. Very often it is screwed after setting up a VPN, installing programs that change network settings.
- WAN Miniport – these are system adapters that Windows needs to connect to the Internet via different protocols (PPTP, PPPoE, L2TP, etc.).
See screenshot:
It may also show “Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter (Microsoft)”, “Virtual Hosted Network Adapter (Microsoft)”, “Kernel Debugging Network Adapter (Microsoft)”. These are all system adapters that are needed for certain functions to work. Most often, this is the Wi-Fi distribution function via the command line, or mobile hotspot in Windows 10.
How to manage network adapters in Windows?
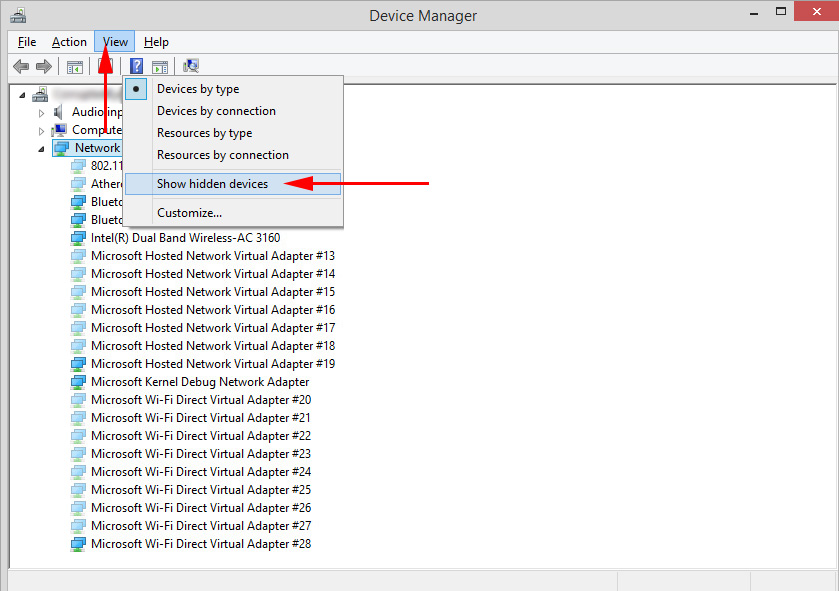
You can click on “View” and check the box next to “Show hidden devices”. After that, all disconnected adapters that were previously connected and configured will appear.
If the icon near the adapter is not bright, but transparent, then it is disabled and cannot be used. If there is an arrow icon near the icon, it means that the adapter is simply turned off. To make it work, we need to activate it (Enable device).
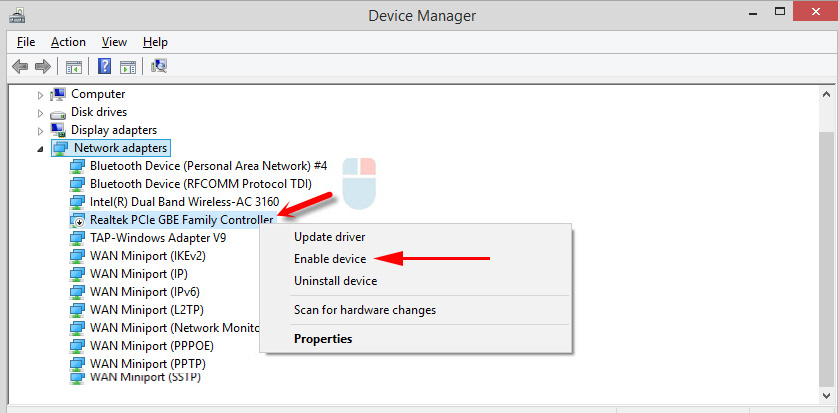
There may also be a yellow exclamation mark near the adapter. This means that the adapter is not working properly. Right click on it and select “Properties”. It will display “Device Status.” There may be an error message and an error code that can be used to find a solution.
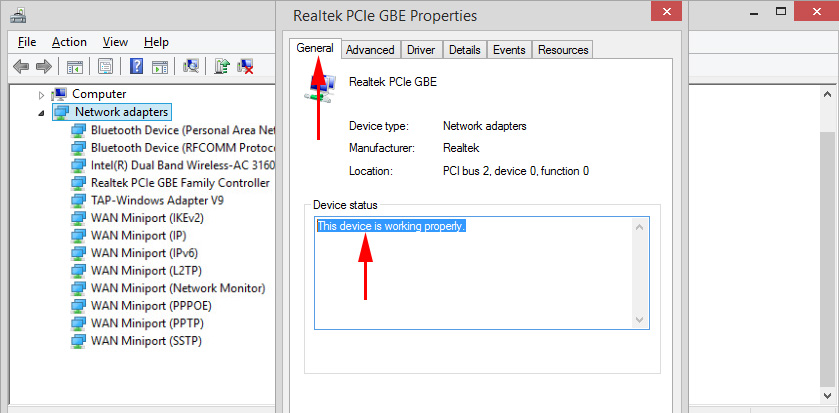
By right clicking on the adapter, you can update its drivers, disable it, or remove it from the system. You can also open the properties (as I showed above) and change the necessary parameters on the corresponding tabs.
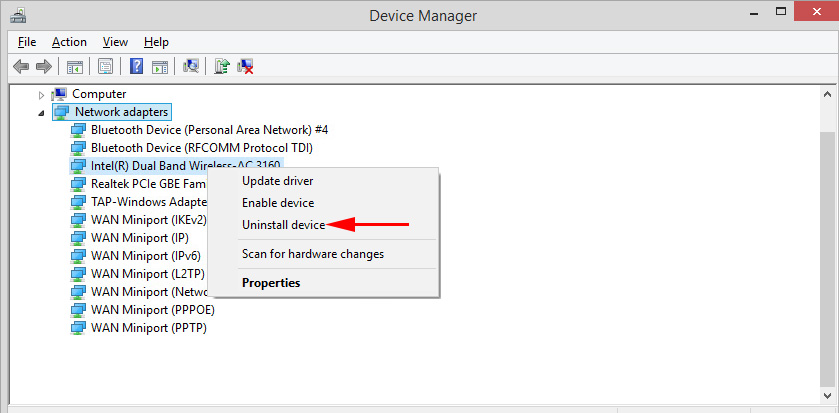
I think that there is no sense to consider all the properties and parameters of each adapter, and they will certainly differ.
Device Manager shows both physical adapters (network card, Wi-Fi module/adapter) and virtual adapters and other components that Windows needs for various functions.
You can open each adapter’s settings, disable it, uninstall it, update drivers, see status, errors, etc. This is exactly what I wanted to show you in this article. If you still have any questions, feel free to ask them in the comments.

 How to Enable or Disable Wi-Fi in the Bios Laptop?
How to Enable or Disable Wi-Fi in the Bios Laptop?  How to Connect a Router to A Laptop?
How to Connect a Router to A Laptop?  AirPlane Mode in Windows 10. How to Disable?
AirPlane Mode in Windows 10. How to Disable?  8.8.8.8 - What Kind of Address? How replace dns with Google Public DNS
8.8.8.8 - What Kind of Address? How replace dns with Google Public DNS